
Composition
- Each Capsule Contains:
- Omeprazole Magnesium IP
20 mg
- Domperidone
10 mg
Packing
- 20x15
(Alu-Strip)
MRP
- 70
Overview
Omeprazole belongs to group of drugs called proton pump inhibitors. It decreases the amount of acid produced in the stomach. Omeprazole is used to treat symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease(GERD) and other conditions caused by excess stomach acid. Domperidone belongs to the group of medications called dopamine antagonists. It is used to treat slowed movement in the gastrointestinal tract associated with diabetes and gastritis(inflammation of the stomach lining). For these people, domperidone improves symptoms of nausea, vomiting, bloating, and feeling of fullness.
WHAT IS ATMOZOLE-D AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR?
ATMOZOLE-D is used to treat the following conditions in adults:
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux Disease
- Dyspepsia
- Nausea and vomiting
- Discomfort caused by a slow moving stomach known as gastroparesis. Symptoms include not being able to finish a meal, a feeling of being "too full" or bloated after a meal, a loss of appetite, feeling sick and maybe vomiting, or belching without relief.
Why is this medication prescribed?
This combination medication contains a proton pump inhibitor and antidopaminergic agent, prescribed for ulcers, indigestion and acid stomach.
Warnings
Some medicines are not suitable for people with certain conditions, and sometimes a medicine may only be used if extra care is taken. For these reasons, before you start taking domperidone it is important that your doctor knows:
If you are pregnant, trying for a baby or breast-feeding.
If you have problems with your liver or kidneys.
If you have problems with your heart or if you have been told you have an irregular heart rhythm.
If you know you have any problems with your digestive system, such as a blockage or any internal bleeding.
If you have a tumour on your pituitary gland known as a prolactinoma.
If you are taking or using any other medicines. This includes any medicines you are taking which are available to buy without a prescription, such as herbal and complementary medicines.
If you have ever had an allergic reaction to any medicine.
Contraindications
Pregnancy, Domperidone is contraindicated in conditions associated with rise in prolactin level. Omeprazole is contraindicated in hypersensitive patients.
Side Effects
Headache, diarrhea, skin rash, itching, abdominal pain, confusion
Dosage
Oral:
Gastro-oesophagealreflux disease, Dyspepsia.
Adult: 1 cap bid or as directed by the physician.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Store the medication as directed by your physician.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Domperidone is a peripheral dopamine D2-receptor antagonist, which regulates the motility of gastric and small intestinal smooth muscle. It increases the duration of antral and duodenal contractions and also LES resting pressure, thus stimulating gastric emptying and is also effective in relief of symptoms of reflux esophagitis. Antiemetic activity is due to the blockade of dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone. Omeprazole inhibits the secretion of gastric acid by irreversibly blocking the enzyme system of H+/K+ATPase of the gastric parietal cell. It is activated at an acidic pH to a sulphenamide derivative that binds irreversibly to H+/K+ ATPase, an enzyme system found at the secretory surface of parietal cells. It thereby inhibits the final transport of hydrogen ions (via exchange with K ions) into the gastric lumen.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:Omeprazole:(because omeprazole is acid-labile), so that absorption of omeprazole begins only after the granules leave the stomach. Absorption is rapid, with peak plasma levels of omeprazole occurring within 0.5 to 3.5 hours. Peak plasma concentrations of omeprazole and AUC are approximately proportional to doses up to 40 mg. Absolute bioavailability (compared with intravenous administration) is about 30-40% at doses of 20-40 mg, due in large part to presystemic metabolism.
Domperidone:Drug is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with peak plasma concentrations at 30 to 60 minutes. The low absolute bioavailability of oral domperidone (15%) is due to an extensive first-pass metabolism in the gut wall and liver. Patients with gastrointestinal complaints should take domperidone 15-30 minutes before a meal. Reduced gastric acidity impairs the absorption of domperidone. Oral bioavailability is decreased by cimetidine and sodium bicarbonate.
Distribution:
Omeprazole:Protein binding is approximately 95%.
Domperidone:Oral domperidone does not appear to accumulate or induce its own metabolism; a peak plasma level after 90 minutes (21ng/ml) after two weeks oral administration of 30 mg per day was almost the same as that of 18 ng/ml after the first dose. Domperidone is 91-93% bound to plasma proteins. It seems to have a good tissue distribution, but low brain concentration. The plasma half life after a single oral dose is 7-9 hours in healthy subjects but is prolonged in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Metabolism:
Omeprazole is extensively metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system.
Domperidone undergoes rapid and extensive hepatic metabolism by hydroxylation (CYP3A4, CYP1A2 and CYP2E1)
Excretion:
Following single dose oral administration of a buffered solution of omeprazole, little if any unchanged drug was excreted in urine. The majority of the dose (about 77%) was eliminated in urine as at least six metabolites. Two were identified as hydroxyomeprazole and the corresponding carboxylic acid. The remainder of the dose was recoverable in feces. This implies a significant biliary excretion of the metabolites of omeprazole.
Domperidone:Urinary and faecal excretions amount to 31 and 66% of the oral dose respectively.
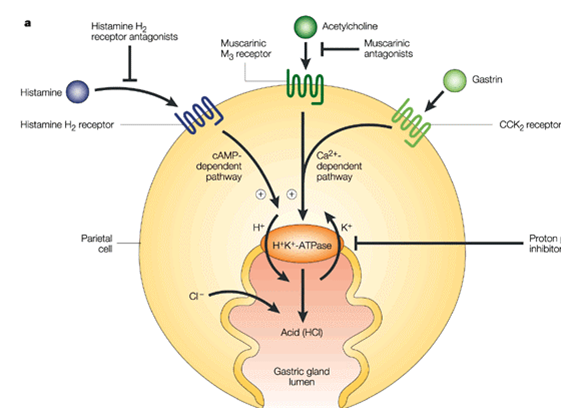
Gastric acid is secreted by parietal cells of the stomach in response to stimuli such as the presence of food in the stomach or intestine and the taste, smell, sight or thought of food. Such stimuli result in the activation of histamine, acetylcholine or gastrin receptors (the H2, M3 and CCK2 receptors, respectively) located in the basolateral membrane of the parietal cell, which initiates signal transduction pathways that converge on the activation of the H+K+-ATPase â€" the final step of acid secretion. Inhibition of this proton pump has the advantage that it will reduce acid secretion independently of how secretion is stimulated, in contrast to other pharmacological approaches to the regulation of acid secretion; for example, the inhibition of acid secretion by H2 receptor antagonists can be overcome by food-induced stimulation of acid secretion via gastrin or acetylcholine receptors. Proton-pump inhibitors such as omeprazole are prodrugs that are converted to their active form in acidic environments. Omeprazole is a weak base, and so specifically concentrates in the acidic secretory canaliculi of the parietal cell, where it is activated by a proton-catalysed process to generate a sulphenamide. The sulphenamide interacts covalently with the sulphydryl groups of cysteine residues in the extracellular domain of the H+K+-ATPase â€" in particular Cys 813 â€" thereby inhibiting its activity. The specific concentration of proton-pump inhibitors such as omeprazole in the secretory canaliculi of the parietal cell is reflected in their favourable side-effect profile.
Interactions
Anticholinergics may antagonize beneficial effects of domperidone in reflux oesophagitis and dyspepsia. Decreased bioavailability of domperidone after prior admin of cimetidine or Na bicarbonate. Delayed elimination of diazepam, phenytoin and warfarin with omeprazole.
For Patient
A risk of unusual heart beat or sudden heart failure has been associated with ATMOZOLE use. The risk is higher in patients older than 60 years or taking more than three tablets daily. ATMOZOLE should be used with caution and should be taken at the lowest effective dose, particularly in older patients. Talk to your doctor if you have a pre-existing heart condition. Treatment with ATMOZOLE should be stopped if signs or symptoms occur that may be associated with unusual heart beat, please talk to your doctor for advice.
Things you must do
- Always follow your doctor's instructions carefully.
- Tell your doctor if you become pregnant while taking ATMOZOLE.
- If you are about to start taking a new medicine, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking ATMOZOLE
Things you must not do
- Do not drive or use machinery or engage in other activities requiring mental alertness or co-ordination until you know how this medication affects you.
- Do not use ATMOZOLE to treat any other complaint unless your doctor says so.
- Do not give this medicine to anyone else, even if their symptoms seem similar to yours.
Chemistry
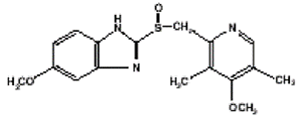
Omeprazole is a substituted benzimidazole, 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3, 5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl) methyl] sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion. Its empirical formula is C17H19N3O3S, with a molecular weight of 345.42. The structural formula is:
Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist (it acts by antagonizing the D2 receptor) with anti-emetic properties. It does not cross the bloodbrain barrier. Its anti-emetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which lies outside the blood-brain barrier in the area postrema

Clinical Data
Clinical Data of Omerprazole
| AU: B3 |
Legal Status | AU: Prescription Only (S4) |
Routes | Oral |
Clinical Data of Domperidone
| Not classified (US) |
Legal Status | N/A |
Routes | Oral |