Composition
- Each Tablet Contains:
- Rabeprazole
20 mg
- Domperidone
10 mg
Packing
- 10x10
(Alu Alu)
MRP
- 68
Overview
Rabeprazole sodium is a substituted benzimidazole and belongs to the class of proton pump inhibitors. Rabeprazole Sodium is an antiulcerant drug in the class of Proton Pump Inhibitors. It suppresses gastric acid secretion by inhibiting the gastric H+/K+-ATPase enzyme at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. It is an enteric coated tablet, because of its coated formulation it is highly stable in stomach and because of higher pKa value of Rabeprazole Sodium it provides faster onset of action.
Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist (it acts by antagonizing the d2 receptor) with anti-emetic properties. It is used to treat slowed movement in the gastrointestinal tract associated with diabetes and gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining). For these people, domperidone improves symptoms of nausea, vomiting, bloating and feeling of fullness.
Indications
- Short-term treatment in healing and symptomatic relief of duodenal ulcers and erosive or ulcerative Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Maintaining healing and reducing relapse rates of heartburn symptoms in patients with GERD.
- Treatment of day time and night time heartburn and other symptoms associated with GERD.
- Long- term treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- Domperidone is used for the relief of nausea and vomiting, epigastric sense of fullness, upper abdominal diacomfort and regurgitation of gastric contents.
- Used to treat nausea and vomiting caused by some drugs (levodopa).
Warning
Rabeprazole
Symptomatic response to therapy with rabeprazole sodium does not preclude the presence of gastric or oesophageal malignancy, therefore the possibility of malignancy should be excluded prior to commencing treatment with rabeprazole.
No evidence of significant drug related safety problems was seen in a study of patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment versus normal age and sex matched controls, the prescriber is advised to exercise caution when treatment with rabeprazole is first initiated in patients with severe hepatic dysfunction.
DomperidoneDomperidone should be used with caution in children, people over 60 years, kidney problems and patient with intolerance to certain sugars.
It should not be used in heart problems, tumor of the pituitary gland, breast feeding and liver problems.
Contraindications
It is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to rabeprazole, domperidone or substituted benzimidazoles or to any excipient used in the formulation.
Contraindicated in patients with hepatic and/or renal impairment, prolactin-releasing pituitary tumour (prolactinoma).
Side Effects
Headache
Upset stomach, mild diarrhea
Insomnia or nervousness
Rash or itching
Dizziness, confusion
Jerking muscle movements
Fast or uneven heart rate
Dry mouth
Stomach cramps
Hot flashes and leg cramps
Nervousness
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:1 tablet daily or as directed by physician
It should be swallowed whole and not be chewed or crushed
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Store in a cool, dry & dark place.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Rabeprazole sodium suppresses gastric acid secretion by the specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme (proton pump) at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell thereby blocking the final step of acid production. This effect is dose-related and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated acid secretion irrespective of the stimulus. Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist (it acts by antagonizing the D2 receptor) with anti-emetic properties. It does not cross the blood brain barrier. Its anti-emetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which lies outside the blood-brain barrier in the area postrema. Studies in man have shown oral domperidone to increase lower oesophageal pressure, improve antroduodenal motility and accelerate gastric emptying. There is no effect on gastric secretion.Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist with antiemetic properties. Domperidone does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier. Its antiemetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of central dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone which lies in the area postrema and is regarded as being outside the blood-brain barrier.
Pharmacokinetics
RabeprazoleAbsorption: Following oral administration, Rabeprazole is absorbed and can be detected in plasma by 1 hour. Absolute bioavailability for a 20 mg oral tablet of rabeprazole (compared to intravenous administration) is approximately 52%. The effects of food on the absorption of rabeprazole have not been evaluated.
Distribution: Rabeprazole is 96.3% bound to human plasma proteins.
Metabolism: Rabeprazole is extensively metabolized. The thioether and sulphone are the primary metabolites measured in human plasma. These metabolites were not observed to have significant antisecretory activity. In vitro studies have demonstrated that rabeprazole is primarily metabolized in the liver by cytochromes P450 3A (sulphone metabolite) and 2C19 (desmethyl rabeprazole). The thioether metabolite is formed by reduction of rabeprazole.
Elimination: Following a single 20 mg oral dose of 14C-labeled rabeprazole, approximately 90% of the drug was eliminated in the urine, primarily as thioether carboxylic acid; its glucuronide, and mercapturic acid metabolites. The remainder of the dose was recovered in in the feces. Total recovery of radioactivity was 99.8%. No unchanged rabeprazole was recovered in the urine or feces.
Domperidone
Absorption: The drug is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with peak plasma concentrations at 30 to 60 minutes. The low absolute bioavailability of oral domperidone (15%) is due to an extensive first-pass metabolism in the gut wall and liver. Patients with gastrointestinal complaints should take domperidone 15-30 minutes before a meal. Reduced gastric acidity impairs the absorption of domperidone. Oral bioavailability is decreased by cimetidine and sodium bicarbonate.
Distribution: Oral domperidone does not appear to accumulate or induce its own metabolism; a peak plasma level after 90 minutes (21ng/ml) after two weeks oral administration of 30 mg per day was almost the same as that of 18 ng/ml after the first dose. Domperidone is 91-93% bound to plasma proteins. It seems to have a good tissue distribution, but low brain concentration. The plasma half life after a single oral dose is 7-9 hours in healthy subjects but is prolonged in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Metabolism: Domperidone undergoes rapid and extensive hepatic metabolism by hydroxylation (CYP3A4, CYP1A2 and CYP2E1) and N-dealkylation (CYP3A4).
Excretion: Urinary and faecal excretions amount to 31 and 66% of the oral dose respectively.
Pharmacodynamics
Rabeprazole belongs to a class of antisecretory compounds (substituted benzimidazole proton-pump inhibitors) that do not exhibit anticholinergic or histamine H2-receptor antagonist properties, but suppress gastric acid secretion by inhibiting the gastric H+, K+ATPase at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. Because this enzyme is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the parietal cell, Rabeprazole has been characterized as a gastric proton-pump inhibitor. Rabeprazole blocks the final step of gastric acid secretion.Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist with antiemetic properties. Domperidone does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier. Its antiemetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of central dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone which lies in the area postrema and is regarded as being outside the blood-brain barrier.
Interactions
Rabeprazole increased gastric pH and has the potential to affect the bioavailability of any medication for which absorption is pH-dependent.
Combinations containing any of the following medications, depending on the amount present, may also interact with this medication.
- Digoxin(rabeprazole may increase gastrointestinal pH; concurrent use with rabeprazole resulted in increase of the serum peak concentration by 29% in normal subjects.
- Ketoconazole(rabeprazole may increase gastrointestinal pH; concurrent use with rabeprazole resulted in 30% reduction of bioavailability.
Chemistry
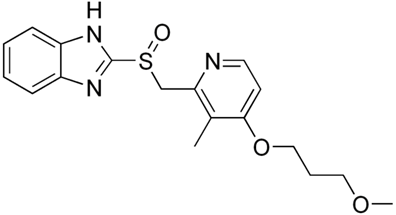
Rabeprazole
Rabeprazole sodium belongs to the class of antisecretory compounds, the substituted benzimidazoles, that do not exhibit anticholinergic or H2 histamine antagonist properties, but suppress gastric acid secretion by the specific inhibition of the H+/K+- ATPase enzyme at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell.
Domperidone
Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist (it acts by antagonizing the D2 receptor) with anti-emetic properties. It does not cross the bloodbrain barrier. Its anti-emetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which lies outside the blood-brain barrier in the area postrema

Clinical Data
Clinical Data Of Domperidone
Pregnancy Category | Not classified (US) |
Legal status | N/A |
Routes | Oral |
Chemical Data
Formula | C15H23N3O4S |
Molecular Mass | 501.68 |
Clinical Data of Rabeprazole
Pregnancy Category | US: B |
Legal status | UK: POM US: Rx-only |
Routes | Oral |
Chemical Data
Formula | C18H21N3O3S |
Molecular Mass | 359.444 g/mol |