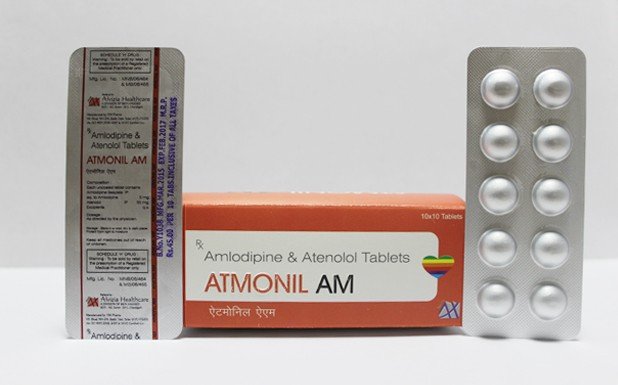
Composition
- Each Uncoated tablet Contains:
- Amlodipine Besylate IP
5 mg
- Atenolol IP
50 mg
Packing
- 10x10
(Alu-Alu)
MRP
- 45
Overview
Amlodipine besilate is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Atenolol is phenylacetamide, a selective Β1 receptor blocker. It blocks the effects of adrenergic stimulation mediated through these receptors.
Rationale of Combination
Amlodipine besilate is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. The contractile process of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine besilate inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. It acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure. Atenolol is phenylacetamide, a selective Β1 receptor blocker. It blocks the effects of adrenergic stimulation mediated through these receptors. The cardio-selectivity is dose related. Atenolol causes a reduction in blood pressure by lowering cardiac output, decreasing the plasma renin activity and sympathetic outflow from CNS. Atenolol also causes a reduction in myocardial oxygen demand by virtue of its negative inotropic and negative chronotropic effects.
Indications
• Antihypertensive activity
• Angina pectoris
• Acute Myocardial Infarction
• Coronary heart disease
Warnings
Care must be exercised in patients with heart failure because of the negative inotropic effects of atenolol. Close monitoring for progressive failure is essential. Similarly, care must be taken with patients with poor cardiac reserve.
Ischaemic Heart disease: especially in patients with ischaemic heart disease, treatment should not be discontinued suddenly. The dosage should be gradually reduced, i.e. over 1-2 weeks, if necessary at the same time initiating replacement therapy, to prevent exacerbation of angina pectoris.
Overdosage may cause hypotension and less commonly, congestive cardiac failure. Unabsorbed drug may be removed by gastric lavage or use of activated charcoal. Symptomatic treatment may be administered.Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with Hypotension, sinus bradycardia, 2nd & 3rd degrees of heart block, cardiogenic shock, overt congestive failure, poor LV function, hypersensitivity to either component, pregnancy.
Side Effects
The combination of amlodipine and atenolol is well tolerated. Side effects include headache, palpitations, flushing, edema, depression.
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:1 tab once daily, may increase to 2 tablets daily if needed. Consult doctor before taking nay medicine.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Store in cool and dry place.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Amlodipine is a calcium ion influx inhibitor of the dihydropyridine group (calcium ion antagonist) and inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle. The mechanism of the antihypertensive action is due to a direct relaxant effect on vascular smooth muscle. Amlodipine reduces total ischaemic burden by the following actions:• Amlodipine dilates peripheral arterioles and thus, reduces the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the heart works. Since the heart rate remains stable, this unloading of the heart reduces myocardial energy consumption and oxygen requirements.
• The mechanism of action of Amlodipine also probably involves dilatation of the main coronary arteries and coronary arterioles, both in normal and ischaemic regions. This dilation increases myocardial oxygen delivery in patients with coronary artery spasm.
Atenolol is a beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent which is cardio-selective; its principal action is on beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart. It is without intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane stabilising activities and as with other beta-blockers, has negative inotropic effects. It is probably assumed that the action of atenolol in reducing cardiac rate and contractility which makes it effective in eliminating or reducing the symptoms of patients with angina.
Pharmacokinetics
AmlodipineAbsorption: After oral administration, Amlodipine is well absorbed with peak plasma levels between 6-12 hours. Plasma levels peak 6-12 hr after oral administration; bioavailability is estimated to be 64-90%.
Distribution: Absolute bioavailability of the unchanged active substance is estimated to be 64-80%. Peak plasma levels are reached 6-12 hours after administration. The volume of distribution is approximately 21 l/kg. In vitro studies have shown that amlodipine is bound to plasmatic proteins up to 97.5%.
Metabolism: About 90% converted to inactive metabolites hepatically.
Excretion: 10% of parent compound and 60% of the metabolites are removed in the urine; elimination from the plasma is biphasic with terminal half-life of about 30-50 hr.
Atenolol
Absorption: Absorption is rapid and with half life of 6-7 hr; about 50% of an oral dose is absorbed in the GI tract; plasma levels peak 2-4 hr after oral administration.
Distribution: only small amounts are reported to cross the blood-brain barrier and plasma-protein binding is minimal (approximately 6-16%). The plasma half-life is about 6-7 hours but this may rise in severe renal impairment since the kidney is the major route of elimination.
Metabolism: Atenolol undergoes little or no hepatic metabolism and more than 90% of that absorbed reaches systemic circulation unaltered.
Elimination: 50% of the oral dose is removed unchanged in the faeces; absorbed drug is removed mainly via renal elimination; half-life is about 6-7 hr.
Interactions
Disopyramide: Atenolol reduces the clearance of disopyramide by 20%. Additive negative inotropic effects on the heart may be produced.Ampicillin at doses of 1 g and above may reduce atenolol levels.
Oral antidiabetics and insulin:Β-blockers may decrease tissue sensitivity to insulin and inhibit insulin secretion e.g. in response to oral antidiabetics. Atenolol has less potential for these actions.
USE IN PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Pregnancy: The combination should be used during pregnancy only if the expected benefit outweighs the potential foetal risk.
Lactation: The combination should not be used by nursing mothers. If its use is considered necessary, breast feeding should be stopped.
For Patients
What should I know before taking the medicine?
Some medicines are not suitable for people with certain conditions, and sometimes a medicine may only be used if extra care is taken. For these reasons, before you start taking Atenolol & Amlodipine it is important that your doctor knows:
- If you are pregnant, trying for a baby or breast-feeding.
- If you have ever had an allergic reaction to Atenolol & Amlodipine or other β antagonist or any calcium channel blocker.
- have heart valve problem called aortic stenosis.
- congestive heart failure
- liver disease. How to take it
- Before you start taking the tablets, read the manufacturer's printed information leaflet from inside the pack. The manufacturer's leaflet will give you more information about Atenolol & Amlodipine and a full list of the side-effects which you may experience from taking it.
- If you do forget to take a dose, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
- If you are being treated for high blood pressure, keep using this medication even if you feel well. High blood pressure often has no symptoms. You may need to use blood pressure medication for the rest of your life.
Chemistry
Atenolol is a selective Β1 receptor antagonist, a drug belonging to the group of beta blockers a class of drugs used primarily in cardiovascular diseases.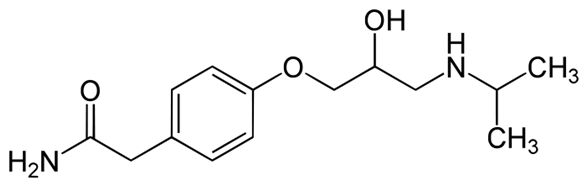
Amlodipine is a medication used to lower blood pressure and prevent chest pain. It belongs to a group of medications known as long-acting dihydropyridine-type calcium channel blockers. Like other medications in this group, amlodipine lowers blood pressure by relaxing the muscles controlling the diameter of blood vessels in the body.
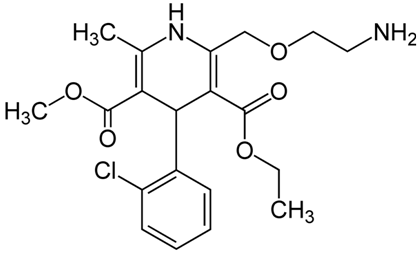
Chemical Name: (RS)-3-ethyl 5-methyl 2-[(2-aminoethoxy) methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
Clinical Data
Clinical Data For Atenolol
Pregnancy Category |
AU: C US: D |
Legal Status | Rx only |
Routes | Oral |
Formula | C14H22N2O3 |
Molecular mass |
266.336 g/mol |
Clinical Data For Amlodipine
Pregnancy category |
AU: C |
Legal Status | UK: POM |
Routes | Oral |
Formula | C20H25CIN2O5 |
Molecular mass |
408.879 g/mol |