Composition
- Each Uncoated Tablet Contains:
- Terbinafine HCL USP
250 mg
Packing
- 10x1x7
(Alu Alu)
MRP
- 135
Overview
ATMOFINE Tablets contain terbinafine which is an anti-fungal agent. ATMOFINE Tablets are used for the treatment of infections such as:
- Fungal infections of the skin and nails
- Ringworm
WHAT IS ATMOFINE AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR?
Terbinafine belongs to a group of medicines called antifungal drugs. Terbinafine tablets are used for the treatment of fungal infections of:
- The groin area.
- The skin (ring worm).
- Toe and finger nails (yellow, opaque and thickened nails).
- The feet (athlete's foot).
Why is this medication prescribed?
Terbinafine is used to treat fungal infections of the toenail and fingernail. Terbinafine is in a class of medications called antifungals. It works by stopping the growth of fungi.
Warning
Some medical conditions may interact with terbinafine. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any medical conditions, especially if any of the following apply to you:If you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding.
If you are taking any prescription or nonprescription medicine, herbal preparation, or dietary supplement
If you have allergies to medicines, foods, or other substances
If you have a history of kidney or liver problems, lupus, depression, psoriasis, alcohol abuse or dependence, or blood problems (eg, anemia)
If you have a weakened immune system or low white blood cell counts
Contraindications
Terbinafine hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in individuals with hypersensitivity to terbinafine or to any other ingredients of the formulation.
Side Effects
All medicines may cause side effects, but many people have no, or minor, side effects. Check with your doctor if any of these most COMMON side effects persist or become bothersome:
Diarrhea; gas; headache; indigestion; mild stomach pain; nausea.
Seek medical attention right away if any of these SEVERE side effects occur:
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing or swallowing; tightness in the chest; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, throat, or tongue; unusual hoarseness);
Burning, numbness, or tingling; mental or mood changes (eg, depression, restlessness, sadness, worthlessness); new or worsening symptoms of lupus (eg, butterfly-shaped rash on the face, joint pain, seizures, skin color changes, unusual sensitivity to the sun); pale skin or nail beds; severe muscle or joint pain or tenderness; severe or persistent stomach pain (with or without nausea or vomiting.
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:
Terbinafine hydrochloride Tablets, one 250 mg tablet, should be taken once daily for 6 weeks by patients with finger nail onychomycosis. Terbinafine, one 250 mg tablet, should be taken once daily for 12 weeks by patients with toenail onychomycosis. The optimal clinical effect is seen some months after mycological cure and cessation of treatment. This is related to the period required for outgrowth of healthy nail.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
- Store Terbinafine tablets at 20℃ to 25℃(68℉ to 77℉)
- Keep Terbinafine tablets in a tightly closed container and keep out of the light.
- Keep Terbinafine tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Terbinafine interferes with fungal ergosterol biosynthesis by inhibiting squalene epoxidase in the fungal cell membrane. This leads to a deficiency of ergosterol and an intracellular accumulation of squalene, thus disrupting fungal membrane function and cell wall synthesis, and resulting in fungal cell death. TERBINAFINE
↓
Interferes with fungal ergosterol
↓
Inhibits squalene Epoxidase in the fungal cell membrane
↓
Leads to deficiency of ergosterol and an intracellular accumulation of Squalene thus disrupting fungal membrane function
↓
CELL DEATH
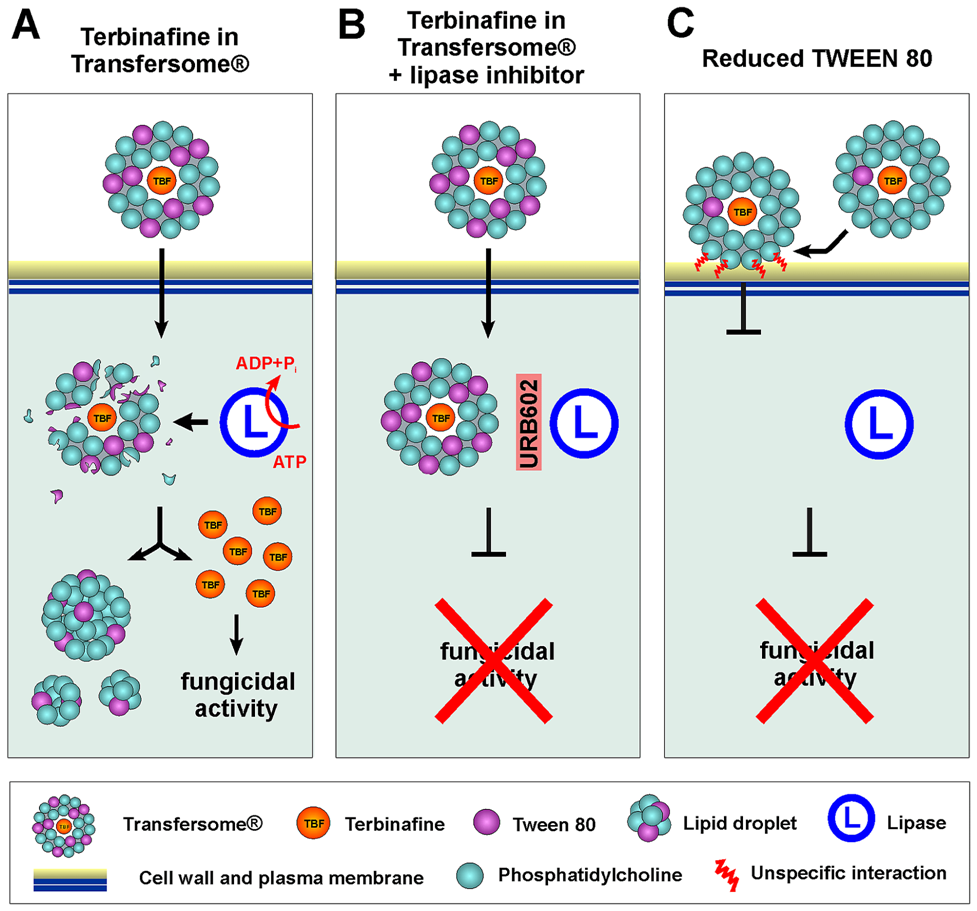
Description: (A) Terbinafine-loaded TFVs contain Tween 80 (purple structures) at high concentration. Tween 80 reduces unspecific interaction with the cell wall and allows extreme deformation of the vesicle membrane, thereby allowing entry of intact TFVs. Once inside the cytoplasm, ATP-dependent cytosolic lipases attack the TFVs and might metabolize Tween 80. This results in collapse of the Transfersome® membranes and the formation of lipid droplets. The digestion of the Transfersome® membranes releases terbinafine in the fungal cell. (B) In the presence of a lipase inhibitor, lipases cannot release the antifungal. Consequently, terbinafine-loaded TFVs are no longer cytotoxic. (C) At lower levels of Tween 80 (phosphatidylcholine to Tween 80 ratio of 20:1 shown here), terbinafine-loaded TFVs enter at much lower rates. Consequently, the vesicles are not degraded and are not cytotoxic.
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, Terbinafine is well absorbed (>70%) and the bioavailability of Terbinafine tablets as a result of first-pass metabolism is approximately 40%. Peak plasma concentrations of 1 µg/mL appear within 2 hours after a single 250 mg dose; the AUC is approximately 4.56 µg.h/mL. An increase in the AUC of Terbinafine of less than 20% is observed when Terbinafine tablets are administered with food.In plasma, Terbinafine is >99% bound to plasma proteins and there are no specific binding sites. At steady-state, in comparison to a single dose, the peak concentration of Terbinafine is 25% higher and plasma AUC increases by a factor of 2.5; the increase in plasma AUC is consistent with an effective half-life of ~36 hours. Terbinafine is distributed to the sebum and skin. A terminal half-life of 200-400 hours may represent the slow elimination of Terbinafine from tissues such as skin and adipose. Prior to excretion, Terbinafine is extensively metabolized by at least 7 CYP isoenzymes with major contributions from CYP2C9, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2C8, and CYP2C19. No metabolites have been identified that have antifungal activity similar to Terbinafine.
Approximately 70% of the administered dose is eliminated in the urine.
In patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance <=50 mL/min) or hepatic cirrhosis, the clearance of Terbinafine is decreased by approximately 50% compared to normal volunteers. No effect of gender on the blood levels of Terbinafine was detected in clinical trials. No clinically relevant age-dependent changes in steady-state plasma concentrations of Terbinafine have been reported.
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of Terbinafine tablets is unknown.Interactions
Some medicines can interfere with your treatment. Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- Rifampicin for infections
- Cimetidine for gastric problems such as indigestion or ulcer
- Antidepressants including tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), or MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors).
- Oral contraceptives (as irregular periods and breakthrough bleeding may occur in some female patients).
- Beta-blockers or anti-arrhythmics for heart problems.
- Warfarin, a medicine used to thin your blood
- Medicines to treat heart problems (eg propafenone, amiodarone)
- Medicines used to treat cough (eg dextromethorphan).
- Caffeine
For Patient
Patients taking Terbinafine tablets should receive the following information and instructions:- Advise patients to immediately report to their physician or get emergency help if they experience any of the following symptoms: hives, mouth sores, blistering and peeling of skin, swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty swallowing or breathing. Terbinafine tablets treatment should be discontinued.
- Advise patients to immediately report to their physician any symptoms of persistent nausea, anorexia, fatigue, vomiting, right upper abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, or pale stools. Terbinafine tablets treatment should be discontinued.
- Advise patients to report to their physician any signs of taste disturbance, smell disturbance and/or depressive symptoms, fever, skin eruption, lymph node enlargement, erythema, scaling, loss of pigment, and unusual photosensitivity that can result in a rash. Terbinafine tablets treatment should be discontinued.
- Advise patients to minimize exposure to natural and artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using Terbinafine tablets.
- Advise patients that if they forget to take Terbinafine tablets to take their tablets as soon as they remember, unless it is less than 4 hours before the next dose is due. Advise patients to call their physician if they take too many Terbinafine tablets.
Chemistry
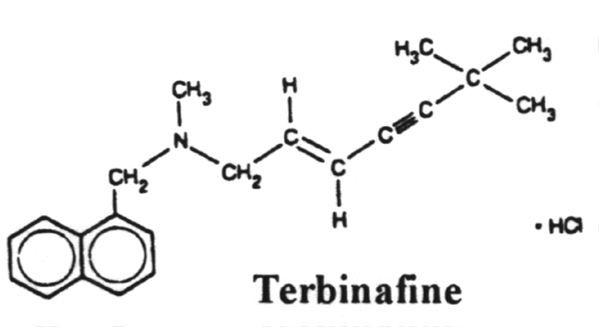
Terbinafine hydrochloride tablets) Tablets contain the synthetic allylamine antifungal compound terbinafine hydrochloride. Chemically, terbinafine hydrochloride is (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1- naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride. The empirical formula C21H26CIN with a molecular weight of 327.90, and the following structural formula: Terbinafine hydrochloride is a white to off-white fine crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in methanol and methylene chloride, soluble in ethanol, and slightly soluble in water.
Clinical Data
Pregnancy category | B |
Legal status | Low-strength preparations available without prescription |
Routes | Oral |