Composition
- Each Uncoated Tablet Contains:
- Albendazole IP
400 mg
- Ivermectin IP
6 mg
Packing
- 6x5x1
(Blister)
MRP
- 19.5
Overview
Albendazole is used to treat neurocysticercosis (infection caused by the pork tapeworm in the muscles, brain, and eyes that may cause seizures, brain swelling, and vision problems). It is also used along with surgery to treat cystic hydatid disease (infection caused by the dog tapeworm in the liver, lung, and lining of the abdomen that may damage these organs). It is in a class of medications called antihelmintics. It works by killing the worm. Ivermectin is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent,traditionally against Parasitic Worms.It is mainly used in humans in the treatment of onchocerciasis (river blindness), but is also effective against other worm infestations(such as strongyloidiasis,ascariasis,trichuriasis,filariasis and enterobiasis)and some epidermal parasitic skin diseases including scabies.
Warnings
In case of Albendazole:
Keep an eye on blood cell counts as well as the functioning of the liver at the start of each 28-day cycle of treatment and every 2 week during treatment period. Stop treatment if liver enzymes are considerably amplified.
To make sure albendazole is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
• Liver disease; or
• Bone marrow suppression
In case of missed dose: Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip it if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
In case of Ivermectin:
Before taking ivermectin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it;
In case of overdose of ivermectin, contact your local poison control center , or emergency room immediately. Symptoms may include abnormal skin sensations; diarrhea; loss of coordination; nausea; seizures; severe headache or dizziness; stomach pain; swelling; trouble breathing; unusual weakness; vomiting.
Contraindications
This combination is contraindicated in case of:
Pregnancy
Lactation
Hypersensitivity
Children < 5 years
Side Effects
Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, pruritus (Itching), skin rash, arthralgia (joint pain), fever, myalgia (muscle pain), asthenia (weakness), tachycardia, oedema, sore throat, cough, headache.
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:
Adult: Per tab contains Ivermectin 6 mg and Albendazole 400 mg: 1 tablet once daily
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Store at room temperature.
Store in cool and dry place.
Protect from heat and light.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Albendazole causes degenerative alterations in the tegument and intestinal cells of the worm by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin, thus inhibiting its polymerization or assembly into microtubules. The loss of the cytoplasmic microtubules leads to impaired uptake of glucose by the larval and adult stages of the susceptible parasites, and depletes their glycogen stores. Degenerative changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria of the germinal layer, and the subsequent release of lysosomes result in decreased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy required for the survival of the helminth. Due to diminished energy production, the parasite is immobilized and eventually dies.
Ivermectin kills the larval Onchocerca volvulus worms microfilariae that live in the subcutaneous tissue of an infected person. It is believed to paralyse or kill the microfilariae gradually, so avoiding the intense inflammatory responses induced when they die naturally. Treatment with ivermectin relieves intense skin itching and halts the progression towards blindness.
Pharmacokinetics
Albendazole:
Absorption:
Albendazole is poorly absorbed from the GI tract; however, it is rapidly converted to its primary active metabolite, albendazole sulfoxide, and prior to reaching systemic circulation. Fatty meals enhance bioavailability, as indicated by up to a 5-fold increase in plasma concentration in albendazole sulfoxide. Albendazole sulfoxide plasma concentrations are dose dependent. Cmax is achieved in 2 to 5 h and ranges from 0.46 to 1.58 mcg/mL, with a fatty meal.
Distribution:
Albendazole sulfoxide is 70% protein bound and widely distributed throughout the body.
Metabolism:
After metabolism in the liver to albendazole sulfoxide, it is further metabolized to albendazole sulfone and other oxidative metabolites.
Elimination:
Albendazole sulfoxide elimination time is 8 to 12 h. Biliary elimination of albendazole sulfoxide results in biliary concentrations similar to plasma concentration. Urinary excretion is a minor elimination pathway (less than 1%).
Ivermectin:
Following oral administration of ivermectin, plasma concentrations are approximately proportional to the dose. Ivermectin is metabolized in the liver, and ivermectin and/or its metabolites are excreted almost exclusively in the feces over an estimated 12 days, with less than 1% of the administered dose excreted in the urine. The plasma half-life of ivermectin in man is approximately 18 hours following oral administration.
Interactions
In case of Albendazole: Cimetidine increases albendazole metabolism. Serum levels are increased if taken with dexamethasone and praziquantel agent.
In case of Ivermectin: Risk of warfarin side effects may be increased by ivermectin. Some of the products that may interact with this drug include: barbiturates (such as phenobarbital, butalbital), benzodiazepines (such as clonazepam, diazepam, lorazepam), sodium oxybate (GHB), valproic acid.
For Patients
Information for Patients:- Take this medication exactly as it was prescribed for you. Do not take the medication in larger amounts, or take it for longer than recommended by your doctor. Follow the directions on your prescription label.
- If you have trouble swallowing a tablet, you may crush the tablet and then drink a full glass of water to swallow it.
- Your symptoms may get better before the infection is completely treated. Complete the course. Take this medication for the entire length of time prescribed by your doctor.
- Albendazole can lower the blood cells that help your body fight infections. To be sure your blood cells do not get too low; your blood will need to be tested on a regular basis. Your liver function may also need to be tested. In case of ivermectin, a sample of your stool (bowel movement) will need to be checked on a regular basis. It is important that you not miss any scheduled visits to your doctor.
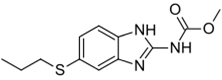
Chemistry
Albendazole is an orally administered broad-spectrum anthelmintic. Chemically, it is methyl 5-(propylthio)-2-benzimidazolecarbamate. Its molecular formula is C12H15N3O2S. Its molecular weight is 265.34. It has the following chemical structure:
Albendazole is a white to off-white powder. It is soluble in dimethylsulfoxide, strong acids, and strong bases. It is slightly soluble in methanol, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and acetonitrile. Albendazole is practically insoluble in water. Ivermectin is a mixture containing at least 90% 5-O demethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a and less than 10% 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro-25-(1-methylethyl)avermectin A1a, generally referred to as 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a and B1b, or H2B1a and H2B1b, respectively. The respective empirical formulas are C48H74O14 and C47H72O14, with molecular weights of 875.10 and 861.07, respectively. The structural formulas are:
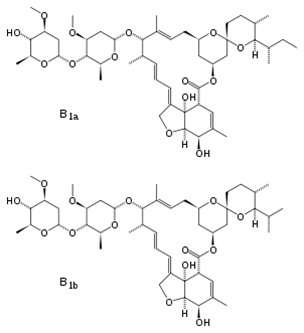
Ivermectin is a white to yellowish-white, nonhygroscopic, crystalline powder with a melting point of about 155°C. It is insoluble in water but is freely soluble in methanol and soluble in 95% ethanol.